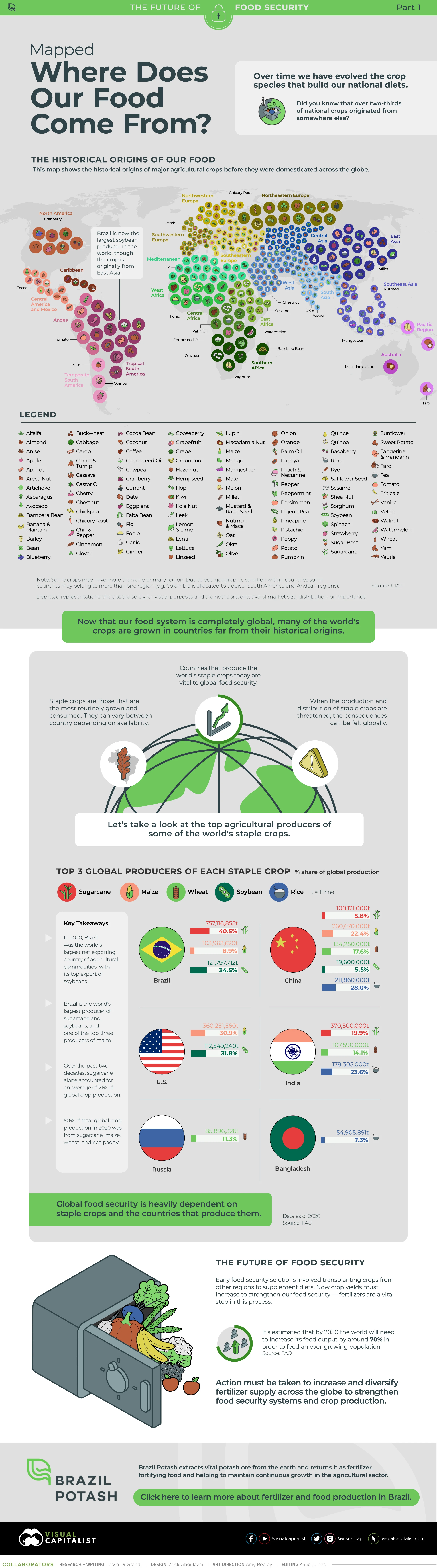
The historical origins of crops before they were domesticated can be traced back to their wild ancestors, which grew naturally in various regions of the world. For example:
- Wheat, barley, lentils, and chickpeas originated in the Fertile Crescent region of the Middle East.
- Corn, beans, and squash were first cultivated in Mesoamerica.
- Rice originated in Asia, with different varieties adapted to different regions such as India, China, and Southeast Asia.
- Potatoes were first domesticated in the Andean region of South America.
- Tomatoes, peppers, and eggplants were first domesticated in the region that includes present-day Mexico and Central America.
- Apples were first domesticated in the region that includes present-day Kazakhstan and China.
The wild ancestors of these crops were adapted to grow in their natural environments without human intervention, and they had traits that allowed them to survive and reproduce in their local ecosystems. Over time, humans began to select and cultivate plants with desirable traits, such as larger seeds or greater yield, which eventually led to the domestication of these crops. The domestication process involved selecting and breeding plants with desirable traits, which allowed crops to be grown more efficiently and in greater quantities, supporting the growth of human civilizations and the development of agriculture as a cornerstone of human society.
Below is the infographic created by Brazil Potash that shows the historical origins of crops before they were domesticated.
This post may contain affiliate links. As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases.
Comments
Post a Comment