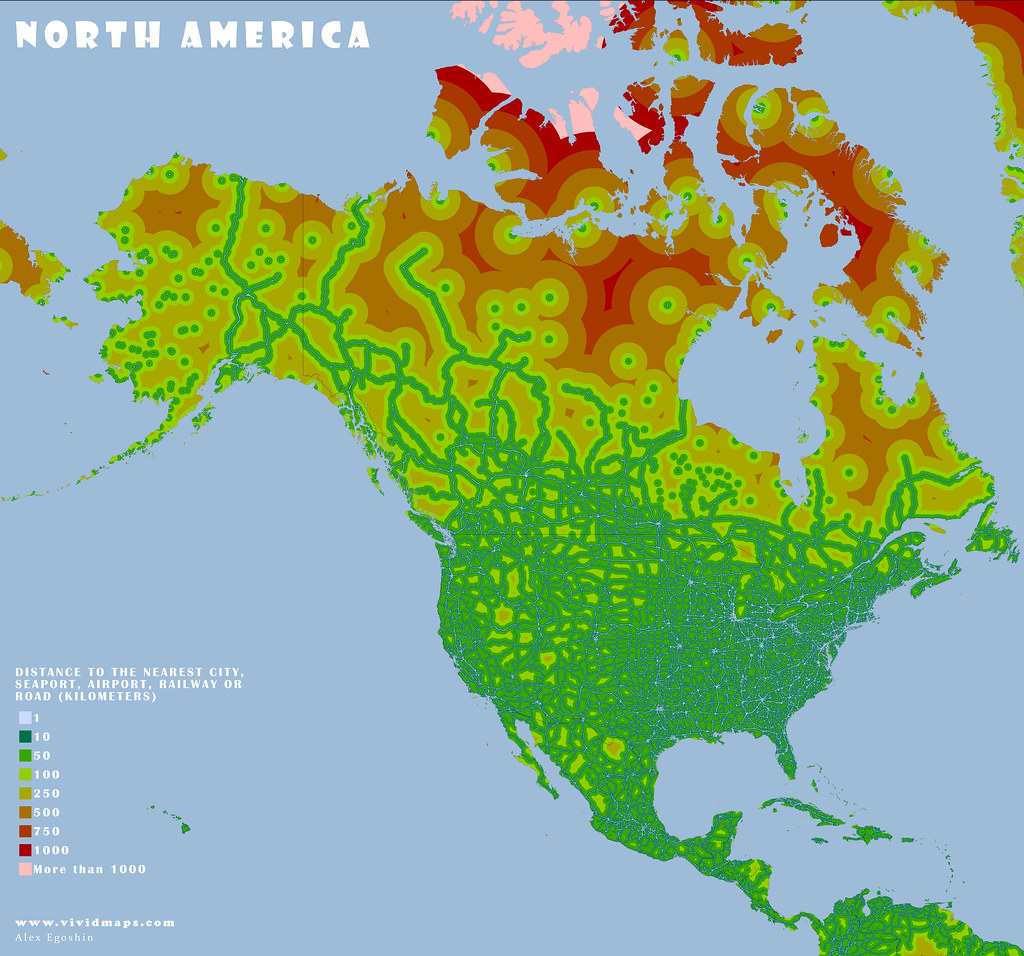
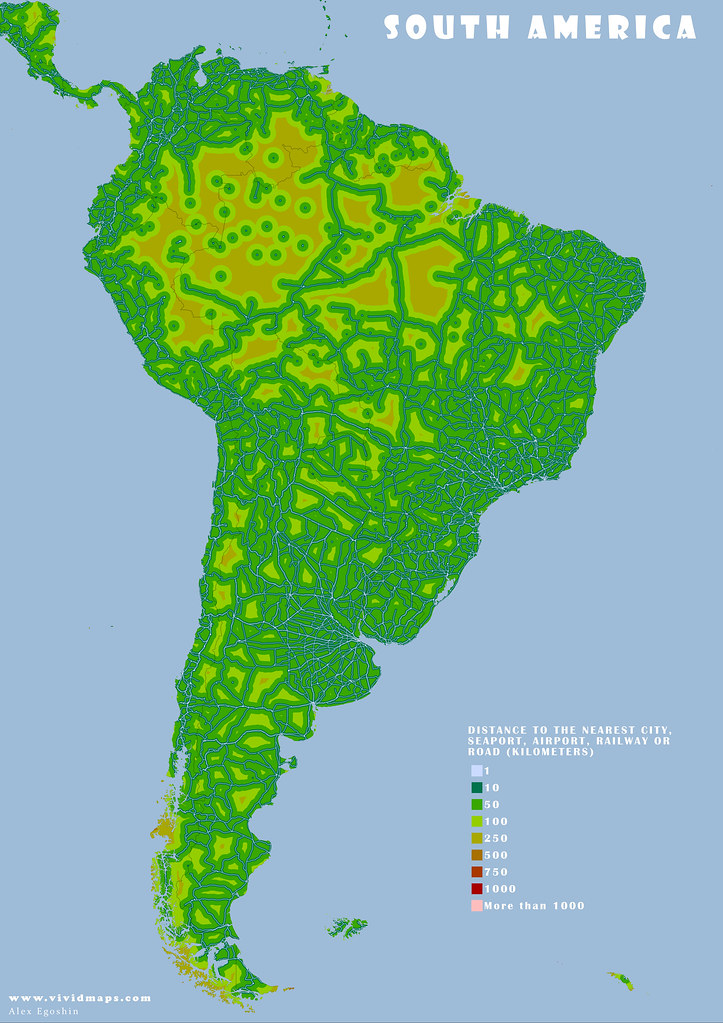
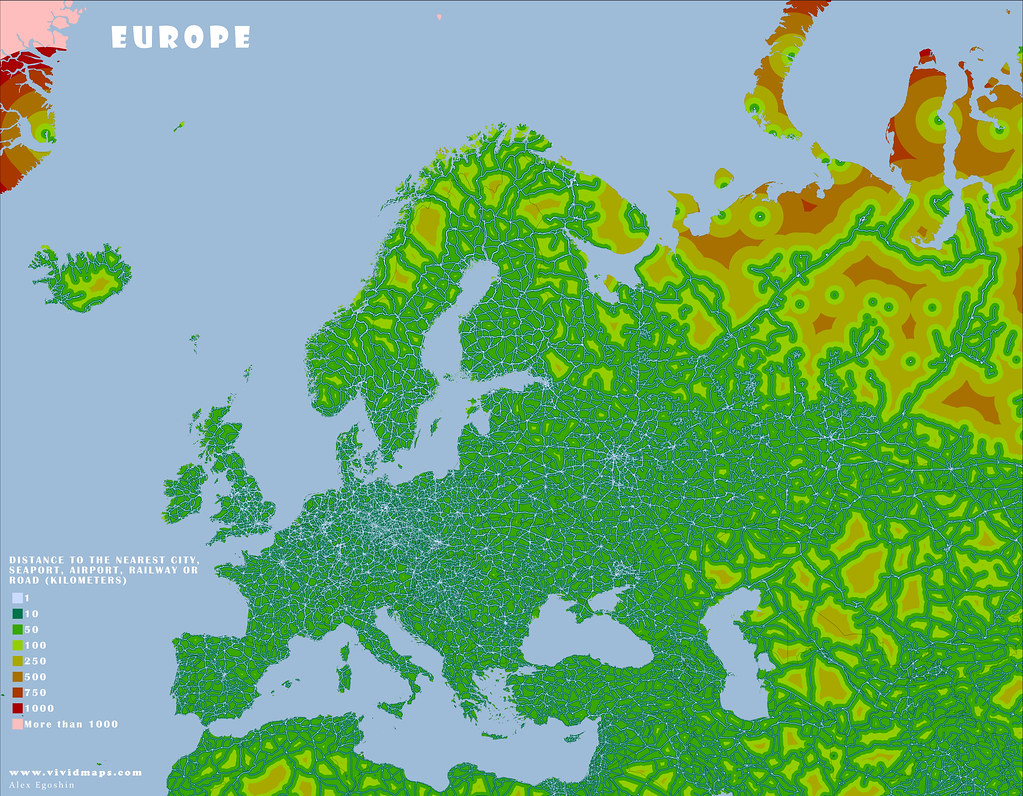
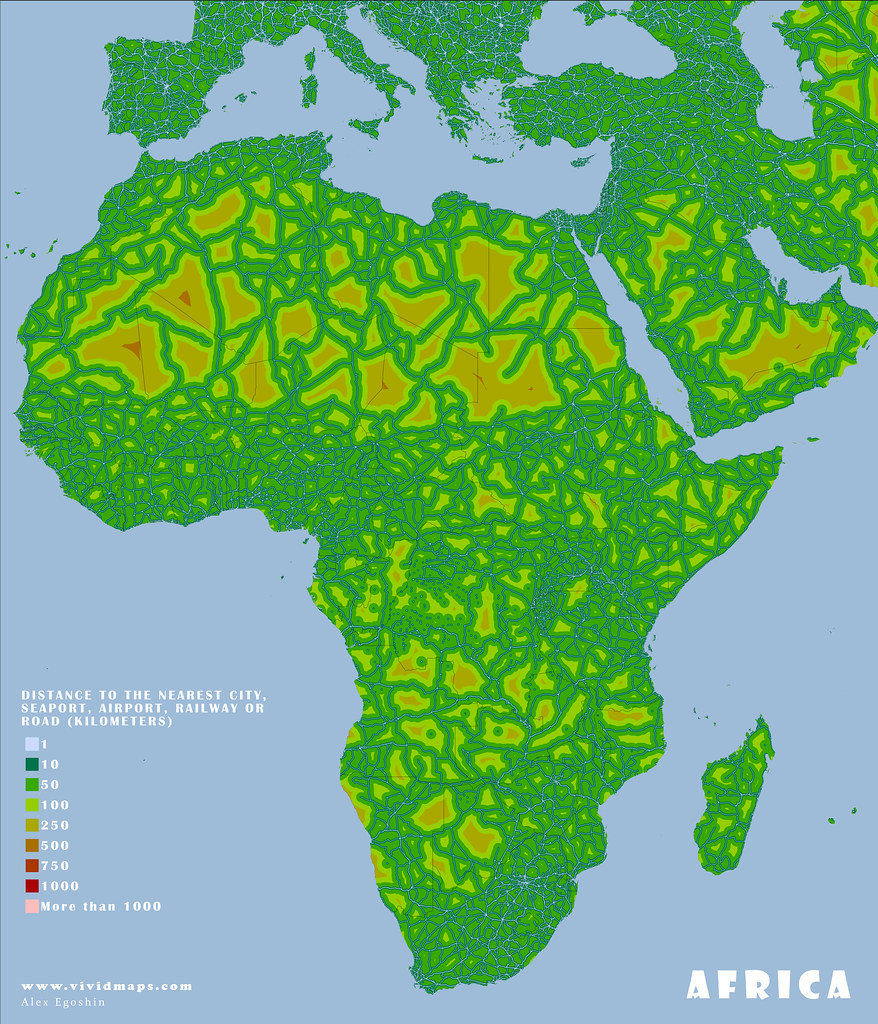
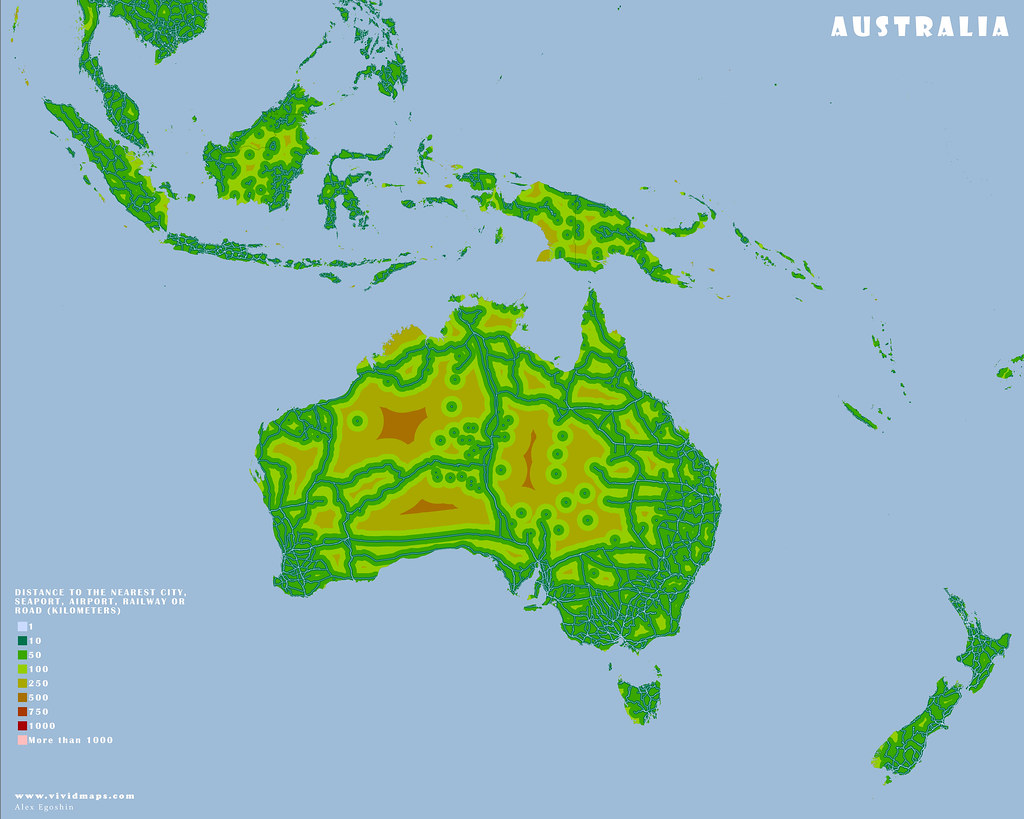
The maps below are based on remoteness from settlements, roads, railroads, and airports. The green areas depict areas where travel to the nearest settlement, road, and other transport facilities can be estimated in hundreds of kilometers.
Most people dwell in red-colored areas, while more than 55% of the global population now resides in urban areas. Only 15% of people in developed countries live more than an hour of driving time from a city.
These maps look like islands in the world ocean. Roads fragment the environment and function as hurdles to cross barriers for living organisms and cause the extinction of numerous species.
Habitat loss, which can happen through habitat fragmentation, is estimated as the greatest threat to species.
Population dynamics of split species populations tend to alter asynchronously. A declining population can be "saved" by migrating from an expanding neighboring population in an unfragmented environment. In a fragmented environment, the barrier within fragments may block this from occurring. Moreover, unoccupied fragments of habitat that are isolated from a source of immigrants by artificial barriers are less supposed to be repopulated.
Also, habitat fragmentation affects edge effects. Microclimatic variations in light, temperature, and wind can change the fragment's environment.
North America
South America
Europe
Asia

Africa
Australia and New Zealand

This post may contain affiliate links. As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases.